How can I stop snoring naturally and sleep peacefully?
If you’re tired of being the reason why your partner wears earplugs—or why you keep waking up feeling foggy and unrested—it’s time to address snoring head-on. Fortunately, many people can significantly reduce or even eliminate their snoring with simple, natural changes that don’t require expensive treatments or procedures.
TL;DR: Summary
- Snoring happens when airflow is partially blocked during sleep, causing vibrations in the soft tissues of the throat.
- The most common symptoms of snoring include loud breathing sounds, dry mouth, fragmented sleep, and morning headaches.
- Major causes of snoring are nasal congestion, excess weight, anatomical issues, sleep position, and alcohol intake.
- Understanding risk factors for snoring helps you identify whether you’re prone to this sleep disorder.
- Untreated snoring can lead to chronic health risks like sleep apnea, high blood pressure, and impaired concentration.
- You can learn how to stop snoring naturally through lifestyle changes like weight loss, positional therapy, and nasal breathing improvements.
- Medical evaluation is essential if snoring is persistent or accompanied by gasping, excessive fatigue, or breathing pauses.
Understanding Snoring and its Impact on Sleep
What is Snoring?
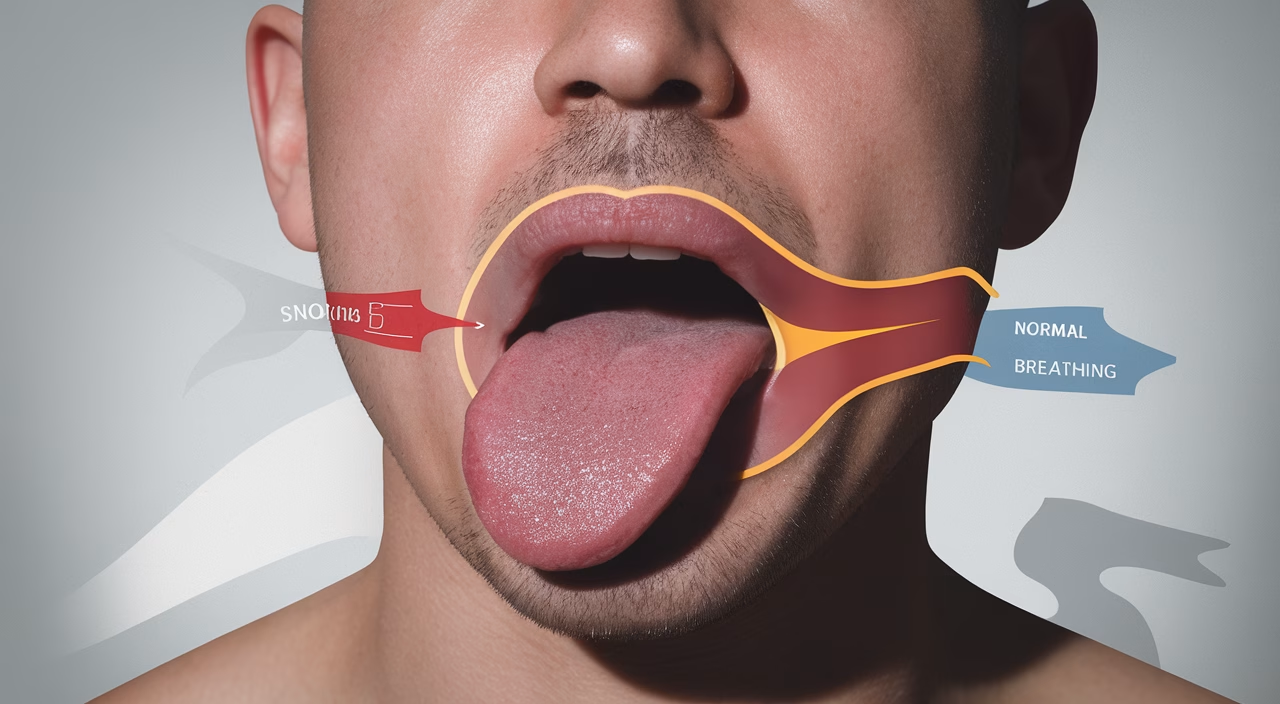
Snoring is the sound produced when air flows past relaxed tissues in your throat, causing them to vibrate as you breathe during sleep. Think of it as a flag fluttering in the wind—when the tissue is loose and air speeds up, sound happens.
While occasional snoring can be harmless, chronic snoring—especially when it’s loud or erratic—is usually a red flag that warrants a closer look at potential underlying sleep disorders.
How Snoring Affects Quality of Sleep
What’s often overlooked about snoring is how disruptive it can be—not only to your bed partner but also to yourself. People who snore may wake themselves hundreds of times a night without realizing it. These micro-awakenings fragment the sleep cycle and prevent deep, restorative rest.
Over time, this leads to poor concentration, memory lapses, mood disturbances, and even weakened immune response. Understanding these effects is crucial when learning how to stop snoring naturally.
Recognizing Symptoms and Common Causes
Common Symptoms of Snoring
If you’ve ever asked someone, “Do I snore?” here are the key symptoms of snoring to look out for:
- Audible snoring—often loud and rhythmic
- Morning headaches or sore throat
- Dry mouth upon waking
- Daytime fatigue or drowsiness
- Witnessed pauses in breathing
- Trouble concentrating or irritability
- Restless sleep and frequent awakening
Major Causes of Snoring
Understanding the causes of snoring is the first step toward finding effective solutions. In clinical experience, the culprits often fall into these main categories:
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Anatomical Factors | Enlarged tonsils, long uvula, or deviated septum |
| Weight Gain | Extra tissue around the neck compresses the airway |
| Sleep Posture | Sleeping on your back relaxes throat muscles |
| Nasal Congestion | Breathing through the mouth causes more vibration |
| Alcohol or Sedatives | These relax muscles too much during sleep |
Identifying which causes of snoring apply to you will help determine the most effective snoring remedies for your specific situation.
Understanding Risk Factors for Snoring
Who is Most Likely to Snore?
Certain risk factors for snoring make some people more susceptible than others. Age is a significant factor—as you get older, your throat becomes narrower and muscle tone decreases. Men are also twice as likely to snore as women due to narrower air passages.
Other key risk factors for snoring include:
- Family history of snoring or sleep apnea
- Being overweight or obese
- Having a thick neck circumference
- Chronic nasal congestion or allergies
- Smoking or alcohol consumption
- Certain medications that relax muscles
The Risks and Consequences of Untreated Snoring
Health Risks Associated with Chronic Snoring
Can snoring lead to serious health problems? Absolutely. Chronic snoring is more than just a nightly disturbance—it’s a red flag. Especially when tied to obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), snoring can increase your risk for:
- High blood pressure and cardiovascular disease
- Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome
- Stroke and heart attack
- Depression and anxiety disorders
- Weakened immune system
If these risks sound scary—it’s because they are. Sleep apnea often goes unnoticed for years and silently affects your heart, brain, and overall longevity.
Impact on Daytime Functioning
Poor sleep quality from snoring doesn’t just stay in the bedroom. It follows you throughout the day. People commonly report:
- Difficulty staying awake during meetings or commute
- Mood changes such as anxiety or depression
- Lack of productivity and focus issues
- Relationship friction due to snoring interruptions
- Increased risk of accidents and injuries
The consequences extend into personal and professional lives, making it all the more essential to act early and learn how to stop snoring naturally.
Effective Lifestyle Changes and Remedies for Snoring
Natural Remedies to Reduce Snoring
Let’s dive into proven strategies on how to stop snoring naturally. The good news? Most people see significant improvement with these snoring remedies:
- Reduce weight: Even a 10% weight loss can drastically reduce snoring volume by decreasing tissue around the neck.
- Limit alcohol: Avoid alcohol 3–4 hours before bedtime to prevent excessive muscle relaxation.
- Clear nasal passages: Use a saline rinse or take a warm shower before sleeping to improve airflow.
- Try throat exercises: Exercises that strengthen throat muscles (like pronouncing certain vowels) can help reduce vibration.
- Use humidifiers: Dry air irritates nasal and throat tissues, worsening snoring.
- Stay hydrated: Dehydration makes nasal secretions stickier, contributing to snoring.
Recommended Sleep Positions to Minimize Snoring
Your sleep position can be a total game-changer when learning how to stop snoring naturally. Lying flat on your back allows the tongue and soft palate to fall backward and block the airway. Try these snoring remedies instead:
- Sleep on your side: Use a body pillow to maintain the posture throughout the night.
- Head elevation: Raise your upper body with an extra pillow or bed wedge to improve airflow.
- Positional training: Some devices gently vibrate when you roll on your back, reminding you to shift.
- Tennis ball technique: Tape a tennis ball to the back of your pajama top to prevent back sleeping.
Seeking Professional Help and Treatment Options
When to Consult a Sleep Specialist or ENT Doctor
While natural snoring remedies work for many people, persistent snoring despite lifestyle changes deserves further evaluation. If your partner notices:
- Gasping, choking, or pauses in breathing during sleep
- Excessive daytime sleepiness affecting daily activities
- Loud, disruptive snoring that worsens over time
- Morning headaches or difficulty concentrating
—it’s time you speak with a sleep specialist or ENT. You might need overnight sleep studies to rule out obstructive sleep apnea or other complications that require medical intervention beyond natural remedies.
Available Treatments for Persistent Snoring
If natural snoring remedies don’t provide enough relief, medical treatments like the following may be advised:
| Treatment Option | Effectiveness |
|---|---|
| Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) | Highly effective for OSA-related snoring |
| Oral Appliances | Pull the jaw forward to open airway |
| Laser-assisted Uvuloplasty | Removes or tightens excess tissue |
| Septoplasty | Corrects deviated nasal septum |
| Pillar Procedure | Implants stiffen soft palate |
Cost Guide: Snoring Treatment Options
| Solution Type | Low-End | Mid-Range | High-End |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oral Appliances | $50 | $300 | $2,000+ |
| CPAP devices | $300 | $800 | $2,500 |
| ENT Surgery | $1,500 | $4,000 | $10,000+ |
| Sleep Study | $150 (at-home) | $500 | $3,500 (in-lab) |
Final Thoughts
Learning how to stop snoring naturally is more than solving a nuisance—it’s about protecting your health and improving your quality of life. Whether you’re exploring natural snoring remedies or considering advanced solutions, the path to quieter nights and restorative sleep starts with understanding the symptoms of snoring, causes of snoring, and risk factors for snoring that apply to your situation. Begin by adjusting your habits, exploring proven remedies, and seeking expert help when needed. Remember, small changes today can protect your well-being for years to come.
Frequently Asked Questions
How to know when snoring is bad?
Snoring becomes concerning when it’s loud, frequent, causes choking or gasping, or results in excessive daytime tiredness. It could indicate sleep apnea and should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
What sleep positions reduce snoring?
Sleeping on your side significantly reduces snoring by preventing the tongue from blocking your airway. Using an elevated head position can also help improve airflow and reduce snoring.
Can losing weight really stop snoring?
Yes, weight loss often reduces or eliminates snoring. Fat around the neck compresses airway passages, and losing just 10% of body weight can improve airflow at night and significantly reduce snoring symptoms.
Is snoring always a sign of sleep apnea?
Not always. While snoring is a major symptom of obstructive sleep apnea, some individuals snore without having OSA. A sleep test can provide clarity and determine if treatment is needed.
Are anti-snoring sprays or devices effective?
They can help with mild cases, especially if caused by nasal congestion or soft palate vibration. However, chronic or severe snoring usually requires a multifaceted approach combining several snoring remedies.
What foods or habits make snoring worse?
Alcohol, dairy before bed, and heavy meals can aggravate snoring by relaxing throat muscles or increasing mucus production. Avoiding these can help reduce snoring naturally.
When should I see a doctor about snoring?
If snoring is chronic, affects your energy levels, or your partner notices pauses in breathing, consult a sleep specialist or ENT. Professional evaluation can rule out serious conditions like sleep apnea.